Recent improvements within SAP Master Data Governance
Master data management is a hot topic
Master Data Management is clearly one of THE topics in contemporary IT and business issues. No wonder, organizations are currently focusing on strategic IT challenges:
Digital transformation: impossible without harmonised master data;
Transition to SAP S/4HANA: one of the foundations is optimized master data;
Cloud applications: these require synchronisation of master data across the landscape.
Operational excellence across all departments of an organization is achieved only with consistent master data that helps prevent process disruptions and unreliable analysis.
The above challenges require high quality master data and should be treated as an asset rather than a cost. SAP Master Data Governance can help you with this.
What is SAP Master Data Governance?
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is an advanced, out-of-the-box master data management application, providing pre-configured, domain-specific master data governance. It supports the central creation, modification and distribution of master data across your entire system landscape. It also provides the ability to consolidate all master data across the entire IT landscape.
There are two versions: SAP Master Data Governance on SAP S/4HANA and SAP Master Data Governance (technically based on SAP ERP 6.0).
SAP MDG ensures data integrity in both SAP and non-SAP systems with which it optimizes business processes. This will lead to higher productivity, process consistency and therefore time and money savings.
The most important dimensions within SAP MDG are:
Governance - Enables governance, compliance and transparency of master data through integrated staging, approval and central audit logging of both creation and modification.
Consistency - Enables consistent definition, authorisation and replication of master data. Eliminates error-prone manual maintenance processes for master data in multiple systems.
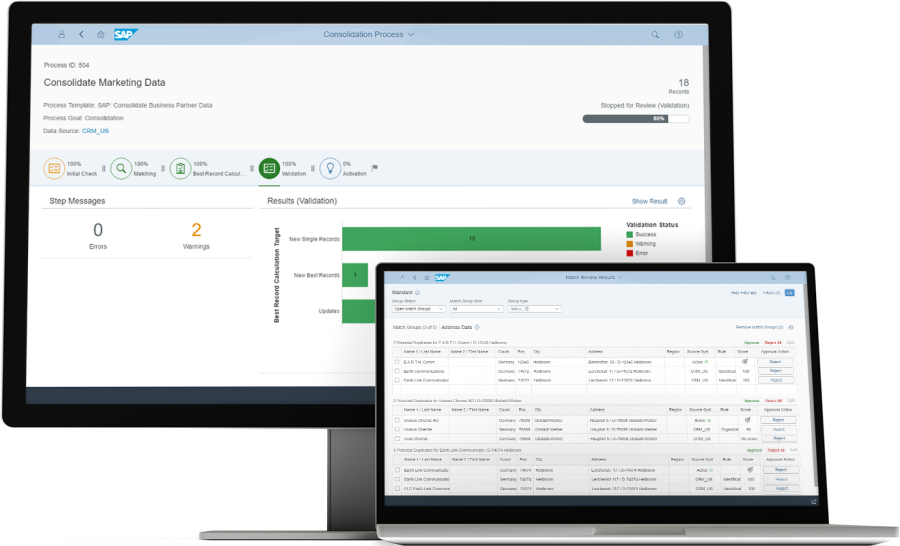
Consolidation - Consolidate master data from your business systems, create best records and key mapping between duplicates, and use centralized management for high quality master data.
Integration - Provides integration with SAP solutions, including reuse of data models, business logic and validation. It is also possible to integrate non-SAP systems.
Flexibility - Standard models can be extended to create governance for proprietary master data from SAP and non-SAP environments.
Data quality - measure process quality using SAP Smart Business and integrate MDG with SAP Data Services & Information Steward. This makes it possible to increase quality, enrich and correct data.
SAP Master Data Governance provides a single application for the complete and central enterprise master data management and provides added value in all domains and all processes. SAP Master Data Governance is the most efficient route to consistent, high-quality master data, the foundation for your digital transformation.
SAP Master Data Governance key features
Consolidation
Create one version of the truth for all your business partners (customers and suppliers), product and financial data.
Mass processing
Make master data stewards more efficient by enabling changes of multiple attributes in multiple business partner, product, and financial records simultaneously.
Central governance
Leverage collaborative workflow routing and notifications so that different teams can own different master data attributes, views, and validated values for the attributes.
Data quality management
SAP Master Data Governance provides robust quality management capabilities for defining, validating, and monitoring domain and process based business rules. It supports proactive data quality checks when creating - for example, automatically validating supplier address data or enriching VAT codes - to avoid the disruptive downstream effect of low data quality. You can monitor data quality through dashboards that show key process indicators of data quality, trends or the distribution of errors across domains or dimensions. This allows you to prioritize your efforts based on impact and business value.
You can define SLAs and monitor master data processes and activities based on statistics. It is possible to set up automated notifications based on threshold values and to perform a root cause analysis based on individual record, change request, workflow step or person.
Process analytics
Measure and monitor master data governance processes.
Enables full master data process transparency;
Get access to dashboards with master data overviews and relevant process information;
Provides user-friendly and detailed insights that bring process quality issues to the surface.
Recent innovations SAP Master Data Governance
Various innovations have been implemented within SAP MDG in recent years. Some recent innovations have only been made available within SAP Master Data Governance on SAP S/4HANA 1809 and 1909. These have not been made available for SAP MDG for SAP ERP.
Innovations within consolidation
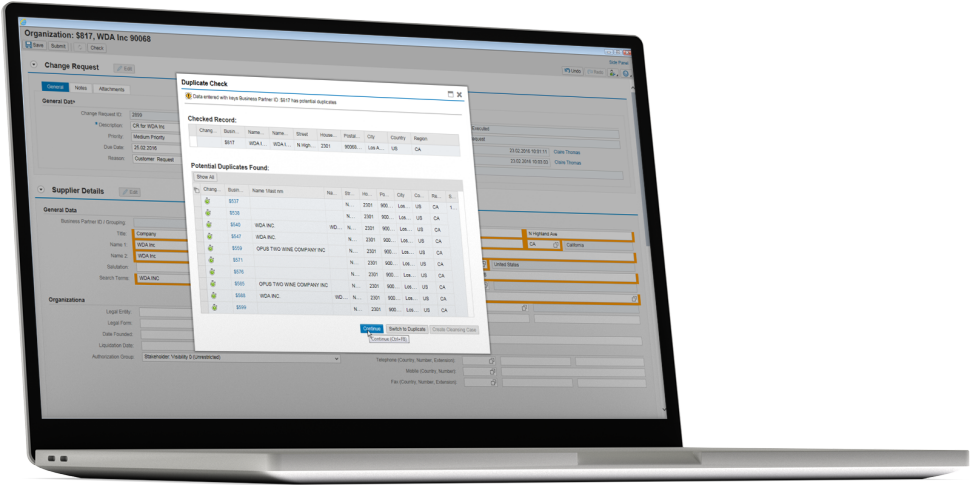
Support allocation of multiple suppliers and customers to a business partner;
Search for changes within active records;
Overview of changes after activation;
Support compressed CSV files to optimize memory usage during loading;
Improved address validation;
Improvements in cross-referencing when loading data from source systems.
The above improves the consolidation of business partners and product data by, among other things, integrating multiple supplier and customer allocations, identifying duplicates and determining the best records.
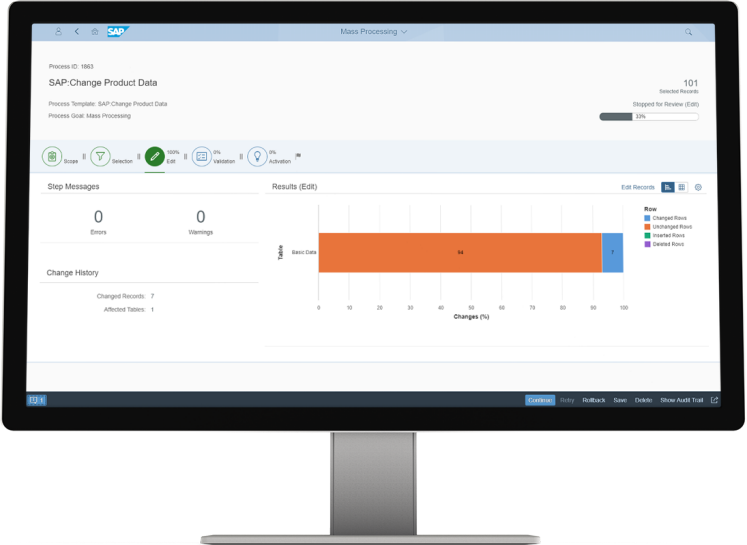
Innovations in mass processing
Support allocations from multiple suppliers and customers to a business partner;
Changing classifications in mass processes;
Export master data to a spreadsheet for offline changes and upload;
Search for changes within active records;
Overview of changes via change documents;
Extensions in data model hedging.
The above results in improvements in the mass implementation of changes of business partners and product data and flexibility in changing classifications.
Innovations within Central Governance
General improvements
SAP MDG on SAP S/4HANA includes the following new functionalities with release 1909:
Improved workflow flexibility and transparency through post-processing steps after activation and follow-up Change Requests;
Change request tracker;
Possibilities to search Change Requests by root data attributes.
Central governance for internal order master data
SAP MDG on SAP S/4HANA includes the following new functionality with release 1809:
Central maintenance and management of internal orders;
Internal order replication via IDOC or SOA1 from the MDG system;
Internal order receipt via IDOC or SOA in SAP S/4HANA, via IDOC in SAP ERP
Initial upload of internal orders in MDG (e.g. from SAP ERP or SAP S/4HANA)
The above enables governance, compliance and transparency of internal orders during creation and modification through integrated staging, approval and central audit logging. It ensures consistent definition, authorization and replication of internal orders and keeps data consistent across systems. It eliminates manual and therefore error-prone maintenance of internal orders across multiple systems.
Cost elements in general ledger
SAP MDG on SAP S/4HANA includes the following new functionality with release 1809:
Central maintenance of control data (cost element) integrated in the general ledger account screen
Replication of cost elements to S/4HANA via the general ledger account (IDOC and SOA service)
The above simplified maintenance of financial master data, harmonizes maintenance as in SAP S/4HANA and simplifies replication to reduce TCO
Improvements object business partners (MDG-BP)
Use newly created customers and suppliers for a business partner as references for partner functions within the same change request
Replication of contract accounts (FI-CA) via SOA (web services)
Improved error messages in UI
Applying business rules from the central rules repository
Improvements object product data/materials (MDG-M)
Various improvements and simplifications within SAP S/4HANA within the domain of product data ;
SAP HANA search has become the default setting for MDG for product data;
Change price units;
Use preferred language for material description in search results list;
Production Resources & Tools fields and relevant SCM fields at MRP area level added to the data model;
Change request processing via inbound Product SOAP messages.
Enrichment via SAP S/4HANA Cloud for Data Enrichment
With SAP S/4HANA Cloud for Data Enrichment, you can enrich master data with name, address and identification information from external data providers. SAP S/4HANA Cloud for Data Enrichment (Data Cloud) is a new DaaS (Data as a Service) solution from SAP to make it possible to consume online data services, for example from Dun & Bradstreet. Business partners, customers or suppliers can be supplemented when creating and modifying existing records.
Innovations within Process analytics
SAP MDG on SAP S/4HANA includes with release 1809 and 1909 improved SAP Fiori user experience in process analytics for master data management including:
Dashboards and analytical tools for an overview of relevant process information
An overview with insight into process quality
Quick access to details for detailed analysis of process quality issues
Innovations within Master data quality management
Business rule mining
With SAP S/4HANA you can use machine learning rule mining to discover data quality rules in existing master data.
Use mining-runs to analyze existing master data
Jointly assess the business relevance of proposed rules from rule mining
Create and link data quality rules based on accepted rules
Information from rule mining can be used in the implementation of data quality rules
Data quality management
SAP MDG on SAP S/4HANA includes with release 1809 data quality management for product data and since 1909 for business partners including:
Repository for definition and categorization of data rules and quality
Maintenance of rules, ownership management and implementation of rules
Collaboration and status handling during rule creation, from creation to activation
"Business rule mining" through the application of machine learning for data analysis and enabling the immediate creation of new business rules based on "mined" rules
Use "Managed data quality rules" for controls within Change Requests (available for Business Partners, scheduled for Product Data)
Export and import of master data quality rules
Analysis data quality
Evaluation of master data using data quality rules
Analysis of incorrect data and correction of identified problems
Definition of data quality scores as KPIs for master data management
Reporting and analysis of quality scores
The above improvements ensure:
Consistent quality definition for product data
Continuous evaluation and monitoring of data quality
MDG roadmap
A master data hub such as MDG that allows master data to be synchronized across on-premise and cloud systems is a requirement when striving to simplify the IT system landscape. It is also an advantage when integrating more and more cloud solutions. SAP therefore puts a lot of time and effort into improving the MDG solution.
The MDG roadmap gives a picture of the vision and direction of the development that SAP pursues. The figure shows the SAP MDG roadmap of December 2019.
For further questions or information on this subject or for other questions in the field of SAP Workflow, Fiori or SAP Invoice Management (SIM), please contact Sander van der Wijngaart.
Related posts

![Recent innovations in SAP MDG [Updated]](https://images.squarespace-cdn.com/content/v1/55378abce4b0be6b204708b1/1568455423784-UA7RH3S6ROG5X0CCC4FR/Data-Center+small.jpg)