Federated MDG
Sander van der Wijngaart - SAP MDG Project Delivery Manager
With the recent launch of Cloud Ready mode in SAP MDG S/4HANA 2023, the concept of Federated MDG is becoming a full-fledged choice as one of the deployment options SAP MDG has to offer. In this tip, we explore the considerations important for organizations striving to professionalize their MDM architecture and tools using the innovative concepts of SAP MDG.
This article will start by highlighting the critical role of master data within an IT landscape and an introduction to SAP MDG. We will then discuss the challenges, solutions and added value of Federated MDG.
Why is master data so important?
Incomplete and/or incorrect master data costs companies a fortune every year. Frustrated users, incorrect system operation and incorrect reporting are the result.
Contemporary managers demand accurate data to support their decisions. Nearly 70% of managers experience errors or deficiencies in the data they use. The numbers speak for themselves; there is still a long way to go. Quality in master data is an issue for all departments within an organization. Solid and correct master data can be seen as a major competitive advantage.
If you experience the following needs:
Full monitoring and integration of your master data across the enterprise
Governance and compliance in master data management processes
Reduction of problems in administrative transactions and reporting
Identification of incorrect master data
Improve the accuracy and reliability of master data analysis
Gain more insight into your master data quality.
Then SAP Master Data Governace (MDG) may be a suitable tool. SAP MDG is a solid master data management SAP Add-on that can fulfill all these requirements.
SAP Master Data Governance
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is an advanced, out-of-the-box master data management solution with domain-specific master data management for centrally maintaining, change and distributing master data. Consolidate all your master data across your entire IT landscape.
SAP MDG ensures master data quality in both SAP and (possibly adjacent) non-SAP systems and thereby optimizes business processes. This will lead to higher productivity, process consistency and time and money savings.
Main functions SAP Master Data Governance:
Central Governance enables you to create and manage master data with centralized workflows that allow you to create, modify and validate master data based on business rules and the manual expertise of domain experts.
Consolidation enables identification of duplicates in decentralized master data and manages key-mapping information to obtain the best record for use in business processes and analysis. Mass processing is designed to efficiently and effectively manage and manipulate large amounts of master data within an organization.
Data Quality Management allows you to actively track and monitor the quality of your master data, and fix problems directly within the application to ensure your data is accurate and reliable.
Of course, MDG also provides extensive standard reporting across these components. This allows the ongoing processes to be managed and monitored from a KPI dashboard, including the ability to zoom in on any deviations.
More general information about SAP Master Data Governance can be found on SAP's website using the following links:
Federated MDG
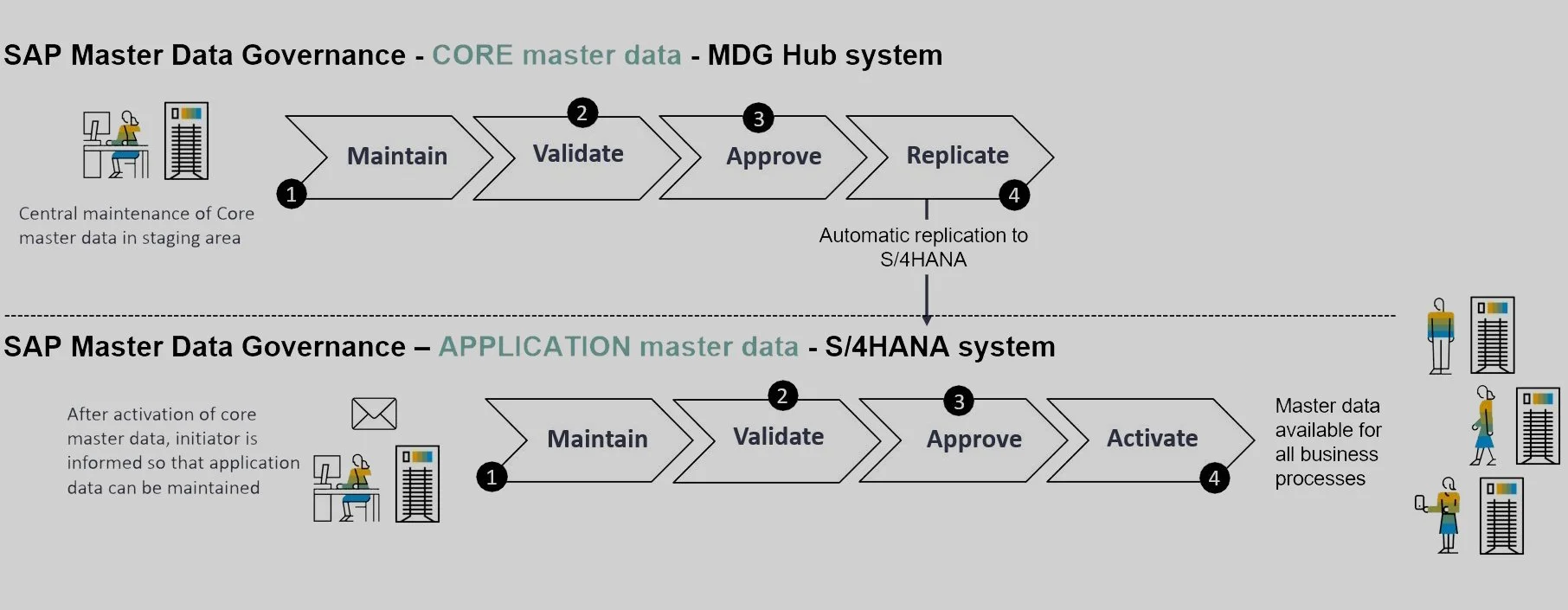
The heterogeneity of business units and complex system landscapes make managing master data at the enterprise level complicated. While core attributes (referred to from here on as Core master data) can be standardized, application-specific (referred to from here on as Application) master data is inherently diverse and difficult to harmonize centrally. This fact highlights the need for a federated approach in Master Data Governance (MDG), balancing central standardization with the unique needs of individual business units.
Distinction in Core and Application master data
Core master data attributes are intrinsic to the definition of domain master data. Core master data include, for example, item description, dimensions and material group. For suppliers and customers (summarized within the business partner concept), these include, for example, address, bank information and tax information.
Application master data includes a rich set of attributes defined differently for each organizational dimension. Examples of application-specific master data include establishment-specific item data such as planning parameters, production versions, and storage location data. For suppliers, we can think of company number-specific data such as payment traffic data and account management. For customers, we can think of sales territory-specific data such as shipping data and partner roles.
These application-specific master data elements are crucial for aligning SAP systems with the unique operational needs of different parts of an organization, contributing to an efficient and smooth business process.
Within Federated MDG, the concepts of Core Data Ownership (CDO) and Application Data Ownership (ADO) are essential to good data management:
Core Data Ownership (CDO).
CDO includes responsibility for the organization's core master data. This data is critical to all business operations and is used across multiple systems and processes. CDO ensures the accuracy, consistency and quality of this data.
Application Data Ownership (ADO).
ADO concerns the management of application-specific master data, tailored to unique business processes or departments. ADO ensures that this data meets the specific requirements of individual applications and remains coherent with the core data managed by CDO.
Problem Statement
A concrete real-life example of a challenge at one of our customers where there was a need to apply Federated MDG is the following. The EMEA organization was using an SAP ECC system where all, i.e. both Core and Application master data, was maintained completely centrally in one S/4HANA MDG Hub system.
When this customer wanted to connect a second S/4HANA system to the central S/4HANA MDG Hub system, it found that there were many hundreds of customizing conflicts that could not be harmonized in the short term. Realize that the fields of materials, customers and suppliers to be maintained involve more than 700 customizing tables. If the master data of the additional system were to be fully managed from the central S/4HANA MDG Hub system, it would mean that all 700 customizing tables and values in the different systems would have to be fully harmonized.
The following figure illustrates the challenge of harmonizing and merging two SAP systems.
If this harmonization and merging is not done properly, replication of MDG change requests will fail. SAP's standard solution at the time was to harmonize all customizing from different systems. This was impossible to achieve for every customizing table. A more pragmatic solution had to be developed to integrate multiple systems with SAP MDG to be ready for future integrations.
The solution
The solution to this problem was found in Federated MDG. Within Federated MDG, data is managed where it is best understood.
Centralized management of Core master data: Core attributes are managed only once, centrally. This ensures a "single source of thruth" and consistency throughout the organization.
Decentralized management of Application master data: Application-specific attributes are managed in the context of the underlying IT systems. Centrally where possible, but as decentralized as necessary. This allows one to do justice to the specific operational reality of each component.
Federated Processes: Federate processes across all IT systems to flexibly meet all needs of both the entire company and individual business units.
The benefits
Embracing a federated approach to MDM brings major benefits, fundamentally transforming the way organizations handle their master data:
Faster value creation: By removing the need for harmonization and enabling underlying IT systems to manage their application-specific data autonomously, organizations can achieve their MDM goals faster.
Increased flexibility: The federated approach enables a more agile MDM strategy that can adapt to the specific needs of connected IT systems without compromising the integrity and consistency of the overall master data.
Broader MDM scope: With less need for prior harmonization and the ability to manage data where it is best understood, organizations can expand the scope of their MDM initiatives, encompassing more diverse and complex data sets and applications.
Prepared for Cloud architecture: Federated MDG correlates with the Cloud-Ready Mode in SAP Master Data Governance and prepares for a more Cloud-based architecture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the federated approach to Master Data Management provides clarity and efficiency in the complex and often chaotic landscape of modern business operations. By managing data where it is best understood and embracing a federated model, organizations can support the complexities of their business units. In doing so, ensuring a cohesive, flexible and efficient MDM strategy across the spectrum of operations.
More information can be found through the following links:
Learn more
For further questions or information on this topic or for other questions on SAP Workflow, Fiori, SAP Invoice Management or SAP Master Data Governance (MDG), please contact Sander van der Wijngaart.
RELATED POSTS